The best manufacturing industry is undergoing a significant transformation, thanks to the emergence of best manufacturing microfactory. These small-scale, highly automated production units are changing the way goods are manufactured, offering unparalleled efficiency, flexibility, and sustainability. But how exactly do best manufacturing microfactory work, and why are they poised to become the future of manufacturing? In this article, we will explore how best manufacturing microfactory will give you the best manufacturing experience, delving into their benefits, applications, and the technology driving this revolution.
What is a Microfactory?
Defining Microfactory
A best manufacturing microfactory is a compact, highly automated facility designed to produce small batches of products efficiently. Unlike traditional factories, which require vast amounts of space and resources, microfactory leverage advanced manufacturing technologies to operate on a much smaller scale. This allows for greater flexibility, reduced environmental impact, and the ability to quickly adapt to changing market demands.
Key Characteristics
best manufacturing Microfactory typically exhibit the following characteristics:
- Compact Size: Microfactory occupy significantly less space compared to traditional manufacturing facilities.
- Automation: High levels of automation reduce the need for human labor, enhancing efficiency and precision.
- Modularity: Components of abest manufacturing microfactory can be easily reconfigured or replaced to accommodate different production needs.
- Sustainability: Reduced resource consumption and waste generation make microfactory environmentally friendly.
- Local Production: Microfactories can be set up close to the end consumer, reducing transportation costs and lead times.
How Microfactories Will Give You Best Manufacturing
Efficiency and Speed
One of the primary advantages of microfactories is their ability to operate with exceptional efficiency. Advanced robotics and automation technologies streamline production processes, minimizing downtime and maximizing output. This results in faster production cycles and the ability to meet tight deadlines, giving businesses a competitive edge in the market.
Flexibility and Customization
Microfactories are designed to be highly adaptable, allowing manufacturers to quickly switch between different products or customize production runs to meet specific customer requirements. This flexibility is particularly valuable in industries where product lifecycles are short, and consumer preferences change rapidly. With microfactories, businesses can respond to market demands with agility, offering customized solutions without the need for extensive retooling.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Sustainability is a growing concern in the manufacturing industry, and microfactories are well-positioned to address this challenge. By operating on a smaller scale and utilizing advanced technologies, microfactories consume less energy and produce less waste compared to traditional manufacturing facilities. Additionally, their ability to be located closer to consumers reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation.
Cost-Effectiveness
The cost of setting up and operating a microfactory is significantly lower than that of a traditional factory. Reduced space requirements, lower labor costs due to automation, and decreased resource consumption all contribute to cost savings. For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), this cost-effectiveness makes microfactories an attractive option, enabling them to compete with larger players in the market.
Enhanced Quality Control
Automation and advanced monitoring systems in microfactories ensure consistent quality throughout the production process. Real-time data collection and analysis enable manufacturers to detect and address issues promptly, reducing the likelihood of defects and ensuring high-quality products. This level of precision and reliability is crucial in industries such as electronics and medical devices, where product quality is paramount.
Image of How microfactory will give you best manufacturing

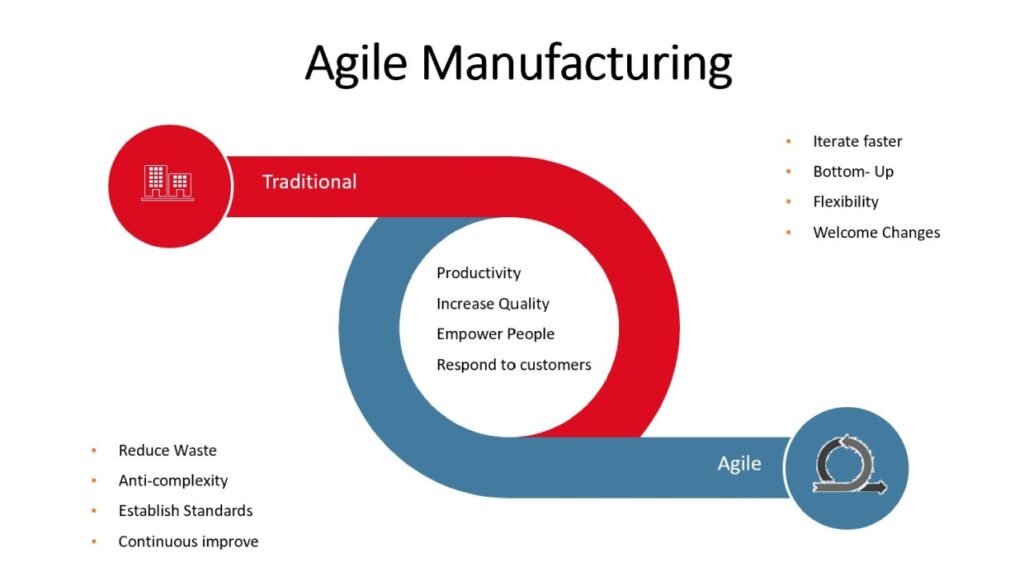

Applications of Microfactories
Electronics Manufacturing
The electronics industry is one of the earliest adopters of microfactory technology. With the rapid pace of innovation and the need for high-quality, customizable products, microfactories offer an ideal solution. From assembling circuit boards to producing consumer electronics, microfactories can handle a wide range of tasks with precision and efficiency.
Automotive Industry
Microfactories are making waves in the automotive industry as well. With the shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) and the increasing demand for customized car parts, microfactories provide a flexible and cost-effective manufacturing solution. Companies can produce small batches of specialized components or even assemble entire vehicles in microfactories, reducing lead times and improving responsiveness to market trends.
Medical Devices
In the medical device sector, precision and quality are of utmost importance. Microfactories excel in producing intricate and high-quality medical devices, such as surgical instruments, implants, and diagnostic equipment. Their ability to quickly adapt to new designs and regulatory requirements makes them invaluable in this highly regulated industry.
Consumer Goods
The versatility of microfactories extends to the production of various consumer goods, including apparel, home appliances, and personal care products. Brands can leverage microfactories to create limited-edition items, test new product lines, or produce goods on-demand, minimizing inventory costs and reducing waste.
Technology Driving Microfactories
Automation and Robotics
At the heart of microfactories lies automation technology. Robotics systems handle tasks ranging from assembly and packaging to quality inspection and inventory management. Advanced robotic arms, autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), and collaborative robots (cobots) work together seamlessly to optimize production processes.
Additive Manufacturing
Also known as 3D printing, additive manufacturing plays a crucial role in microfactories. This technology enables the creation of complex and customized parts with minimal material waste. By integrating 3D printing capabilities, microfactories can produce prototypes, spare parts, and even finished products on-demand, further enhancing their flexibility and efficiency.
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT technology connects various components of a microfactory, enabling real-time monitoring and data collection. Sensors and smart devices gather information on machine performance, production status, and environmental conditions, providing valuable insights for optimizing operations. IoT-enabled microfactories can predict maintenance needs, prevent downtime, and improve overall productivity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI algorithms analyze data collected from various sources within a microfactory, offering predictive insights and optimizing decision-making. From demand forecasting to quality control, AI enhances the efficiency and accuracy of manufacturing processes. Machine learning models can identify patterns, detect anomalies, and recommend improvements, driving continuous optimization.
FAQs
What is the primary advantage of microfactories?
The primary advantage of microfactories is their efficiency and flexibility. They can quickly adapt to changing market demands, produce customized products, and operate with minimal resource consumption.
Are microfactories suitable for all types of manufacturing?
While microfactories are highly versatile, they are particularly well-suited for industries that require high levels of customization, rapid production cycles, and precise quality control. Examples include electronics, automotive, medical devices, and consumer goods.
How do microfactories contribute to sustainability?
Microfactories contribute to sustainability by consuming less energy, producing less waste, and reducing the carbon footprint associated with transportation. Their compact size and efficient use of resources make them an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional factories.
Can small businesses benefit from microfactories?
Yes, small businesses can greatly benefit from microfactories. The lower setup and operational costs, combined with the ability to produce small batches and customized products, make microfactories an attractive option for SMEs.
What role does automation play in microfactories?
Automation is a key component of microfactories. It enhances efficiency, precision, and consistency in production processes, reducing the need for human labor and minimizing the risk of errors.
Conclusion
Microfactories are poised to revolutionize the manufacturing industry, offering a blend of efficiency, flexibility, and sustainability that traditional factories cannot match. By leveraging advanced technologies such as automation, additive manufacturing, IoT, and AI, microfactories can deliver high-quality, customized products with minimal environmental impact. Whether you are a small business looking to compete in a crowded market or a large enterprise seeking to improve responsiveness and reduce costs, microfactories offer a compelling solution. Embrace the future of manufacturing with microfactories and experience the best that modern production has to offer.


