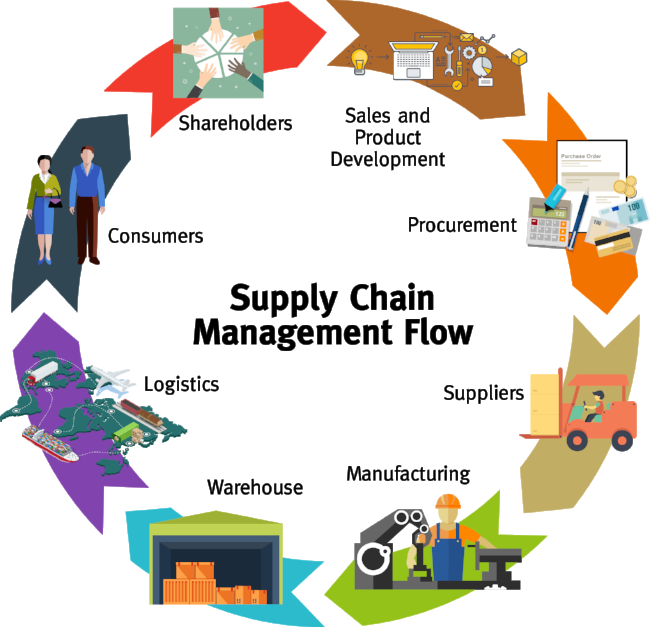
Logistics and Supply Chain Coordination in Manufacturing Operations At its core, logistics involves managing the movement of goods, while Logistics and Supply Chain Coordination in Manufacturing Operations ensures that each step of manufacturing is interconnected. When done right, these two forces work together like a well-oiled machine, reducing delays, cutting costs, and delivering quality products. In manufacturing, logistics and supply chain coordination Manufacturing Operations are not just buzzwords—they’re lifelines.
Table of Contents
The Role of Logistics in Manufacturing
Logistics is all about planning, implementing, and controlling the flow of materials from point A to point B. In manufacturing Operations, it includes everything from sourcing raw materials to delivering finished products to customers. Think of it as the invisible hand guiding the materials across the factory floor and beyond.
Key Functions of Logistics in Manufacturing
To understand the role of logistics, let’s break down the key functions that keep the process running smoothly.
Transportation Management
Ever wondered how products make their way across cities or even countries? Transportation management ensures that goods are moved efficiently, whether by road, air, or sea. Manufacturing Operations must decide on the fastest, most cost-effective way to get their products to market.
Inventory Control and Warehousing
Manufacturing Operations must store materials and finished goods before they’re shipped out. Inventory control ensures that there’s always the right amount of stock—too much, and you waste resources; too little, and you can’t meet demand. Warehousing plays a vital role in storing these materials until they’re needed, keeping everything organized and accessible.
The Importance of Supply Chain Coordination
Now, logistics is important, but it’s only part of the bigger picture. Supply chain coordination ensures that all the cogs in the manufacturing machine work in harmony. Picture it like this: it’s not just about moving pieces but making sure those pieces arrive at the right time and place to avoid costly delays.
Synchronizing Production with Demand
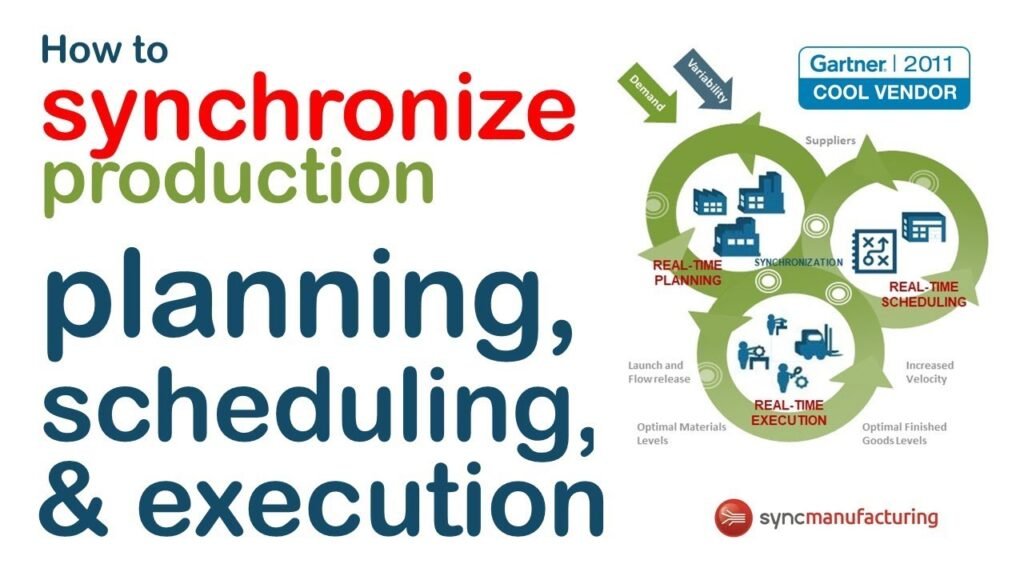
A smooth supply chain starts with aligning production with demand. By predicting how much product will be needed and when, manufacturers can avoid overproduction and stockpiling. This helps reduce waste and keeps the supply chain lean and agile.
Supplier Relationship Management
Strong relationships with suppliers are essential for any manufacturing operation. Without reliable suppliers, even the best-planned logistics will fall apart. By nurturing partnerships and ensuring open lines of communication, manufacturers can secure steady supplies of the raw materials needed to keep the production line moving.
Challenges in Logistics and Supply Chain Coordination
As efficient as logistics and supply chains are, they’re not without their challenges. The key to success lies in identifying and overcoming these obstacles.
Communication Breakdowns
In a globalized world, supply chains are vast and complex, often stretching across countries and continents. A breakdown in communication—whether with suppliers, distributors, or internal teams—can cause delays and errors. Clear communication channels are essential to avoid these pitfalls.
Lack of Real-Time Data
Manufacturing operations rely on accurate, up-to-date information. Without real-time data, companies are left in the dark, reacting to problems rather than preventing them. This can lead to overproduction, missed deadlines, and unhappy customers.
Leveraging Technology in Logistics and Supply Chain
With the rapid pace of technological advancements, logistics and supply chain coordination are becoming smarter and more efficient. The key? Embracing the tech that can transform your operation.
The Role of Automation and AI

Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are game-changers in manufacturing logistics. From self-driving trucks to AI-powered warehouse robots, these technologies can dramatically reduce human error, lower labor costs, and speed up production.
Benefits of Cloud-Based Supply Chain Systems
Cloud-based systems allow manufacturers to access real-time data, communicate effortlessly with suppliers, and manage logistics from anywhere in the world. Imagine having a bird’s eye view of your entire supply chain at your fingertips—that’s what cloud-based systems bring to the table.
The Rise of Microfactory in Manufacturing
Now, let’s talk about microfactory—small, decentralized manufacturing units that are reshaping the future of production. Microfactory are an exciting trend, offering manufacturers flexibility and efficiency on a whole new level.
What are Microfactory?
Microfactory are compact manufacturing spaces, typically highly automated, that produce small quantities of goods tailored to specific markets. These factories are often located closer to consumers, cutting down on transportation costs and lead times. Think of them as bite-sized factories with maximum efficiency.
How Microfactory Revolutionize Supply Chains
Microfactory are turning traditional supply chains upside down. Instead of relying on one large factory to produce goods for an entire market, manufacturers can use multiple microfactory to serve specific regions. This decentralization brings several benefits, including quicker response times, reduced transportation costs, and the ability to cater to local demand.


Sustainability and the Microfactory Model
Microfactory are also more sustainable than their larger counterparts. By producing goods locally and minimizing transportation, they reduce carbon emissions. Additionally, because microfactory focus on small-batch production, they often generate less waste. It’s a win-win for the planet and the bottom line.
Coordination between Microfactory and Traditional Manufacturing
Of course, microfactory don’t exist in a vacuum. They need to work in harmony with traditional manufacturing operations to maximize efficiency. This is where supply chain coordination plays a crucial role.
Integrating Microfactory into Existing Supply Chains
Integrating microfactory into a traditional supply chain requires careful planning. Manufacturers need to ensure that products produced at microfactory meet the same quality standards as those made in larger facilities. Additionally, data and communication must flow freely between all manufacturing units to avoid disruptions.
The Future of Logistics and Supply Chain in Manufacturing

So, where do we go from here? As technology continues to advance, we can expect logistics and supply chains to become even more efficient, with automation, AI, and microfactory leading the charge. The key to success will lie in staying flexible, embracing new technologies, and continuously optimizing operations.
Conclusion
Logistics and supply chain coordination are the unsung heroes of manufacturing operations. Without them, the process of turning raw materials into finished products would be a chaotic, inefficient mess. With the rise of microfactory and the integration of advanced technologies like AI, the future of manufacturing is looking brighter and more streamlined than ever.
FAQs
1. What is the role of logistics in manufacturing?
Logistics in manufacturing involves the efficient movement of materials and goods from suppliers to the factory and from the factory to the end customer, ensuring timely delivery and cost-effectiveness.
2. How do microfactory differ from traditional factories?
Microfactory are smaller, more flexible manufacturing units that focus on small-batch, localized production, whereas traditional factories are large-scale and centralized.
3. Why is supply chain coordination important?
Supply chain coordination ensures that each step of the manufacturing process is synchronized, minimizing delays and improving efficiency by aligning production with demand.
4. How can AI improve logistics in manufacturing?
AI can streamline operations by automating tasks like inventory management, transportation scheduling, and predictive analytics, resulting in fewer errors and faster processes.
5. What are the environmental benefits of microfactory?
Microfactory help reduce carbon emissions