In the quest for a more sustainable future, industries worldwide are embracing the concept of a circular economy. Unlike the traditional linear economy, which follows a ‘take, make, dispose’ model, a circular economy aims to minimize waste and make the most of resources. This shift is not just a trend but a necessity, as the planet’s resources are finite and the environmental impact of waste is increasingly severe. In this article, we’ll delve into the principles of creating a circular economy, with a special focus on sustainable practices in manufacturing.
What is a Circular Economy?
At its core, a circular economy is about closing the loop of product lifecycles. This means designing products that can be reused, repaired, remanufactured, or recycled. The goal is to create a system where resources are kept in use for as long as possible, extracting maximum value before recovering and regenerating products and materials.
The Benefits of a Circular Economy
- Reduced Waste: By reusing and recycling materials, waste is significantly minimized.
- Resource Efficiency: Maximizing the use of resources reduces the need for new raw materials.
- Economic Growth: New business models and job opportunities emerge from innovative recycling and remanufacturing processes.
- Environmental Protection: Less waste and reduced extraction of raw materials lead to lower pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Key Principles of a Circular Economy
To understand how to create a circular economy, it’s important to grasp its foundational principles:
- Design Out Waste and Pollution: Products should be designed to avoid waste and pollution from the outset.
- Keep Products and Materials in Use: Ensure that products and materials are reused, repaired, and recycled.
- Regenerate Natural Systems: Aim to return valuable nutrients to the environment, enhancing biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
Manufacturing plays a critical role in the circular economy. By adopting sustainable practices, manufacturers can contribute significantly to resource efficiency and waste reduction.
Eco-Design
Eco-design is about designing products with their entire lifecycle in mind. This involves choosing materials that are durable, recyclable, and environmentally friendly. Products should be easy to disassemble, so their components can be reused or recycled. For instance, some electronics manufacturers design products that are easy to repair and upgrade, extending their lifespan and reducing electronic waste.
Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing focuses on minimizing waste within manufacturing systems while maximizing productivity. This method involves identifying and eliminating non-value-added activities. Techniques such as just-in-time production, where materials are only ordered and received as they are needed, help reduce inventory waste and improve efficiency.
Renewable Energy Integration
Integrating renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydro power, into manufacturing processes reduces dependence on fossil fuels and lowers carbon footprints. Factories powered by renewable energy can significantly cut their greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a more sustainable manufacturing sector.
Recycling and Remanufacturing
Recycling involves breaking down products at the end of their life cycle to recover valuable materials for reuse. Remanufacturing goes a step further by restoring used products to a like-new condition. This not only reduces waste but also saves energy compared to producing new items from scratch. For example, the automotive industry has embraced remanufacturing by refurbishing used car parts to meet original specifications.
Images of Creating a Circular Economy: Sustainable Practices in Manufacturing
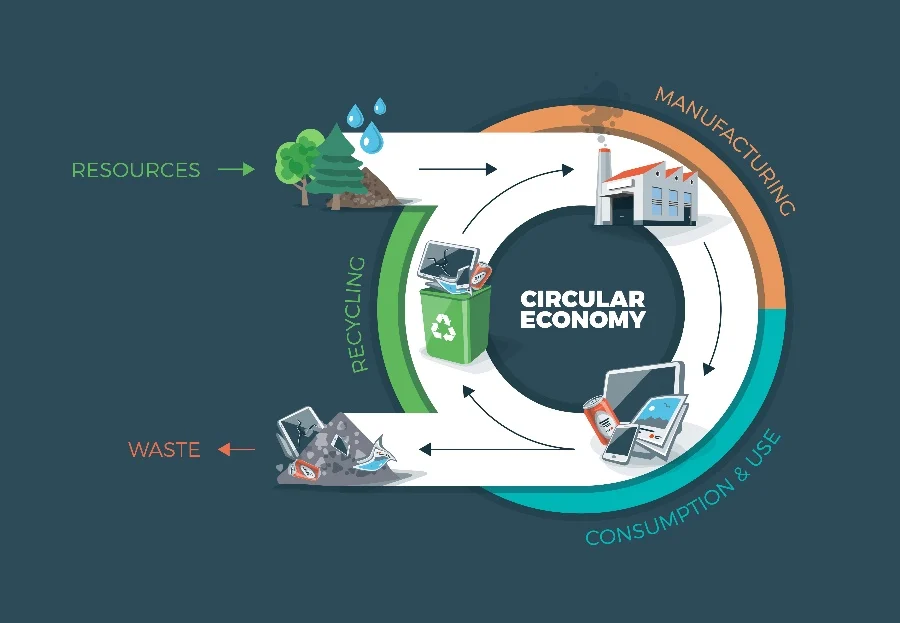
Real-World Examples
Several companies are leading the way in creating a circular economy through innovative sustainable practices.
Patagonia
Patagonia, a well-known outdoor apparel brand, has long been a proponent of sustainability. The company encourages customers to repair their gear instead of replacing it and offers a recycling program for worn-out products. Patagonia also uses recycled materials in its clothing line, reducing the need for virgin resources.
Interface
Interface, a global manufacturer of modular flooring, has implemented a successful circular economy model. The company designs its products for easy disassembly and recycling. Interface also sources materials from recycled products and industrial waste, significantly reducing its environmental impact.
Philips
Philips, a leader in health technology, has embraced circular economy principles in its product design and business models. The company offers services like product leasing, where customers can use equipment and return it for refurbishment or recycling. This approach ensures that products are kept in use longer and materials are recovered at the end of their lifecycle.
Challenges and Opportunities
Transitioning to a circular economy in manufacturing is not without its challenges. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and growth.
Challenges
- Economic Viability: Initial costs of transitioning to sustainable practices can be high, and the economic benefits may take time to materialize.
- Technological Barriers: Developing new technologies for recycling and remanufacturing can be complex and resource-intensive.
- Consumer Behavior: Encouraging consumers to adopt circular economy principles, such as returning products for recycling or choosing refurbished items, requires significant effort.
Opportunities
- Innovation: The shift towards a circular economy drives innovation in product design, materials science, and manufacturing processes.
- New Business Models: Companies can develop new business models, such as product-as-a-service or leasing, which offer ongoing revenue streams and strengthen customer relationships.
- Policy and Regulation: Governments and international bodies are increasingly supporting circular economy initiatives through policies and incentives, creating a favorable environment for businesses to adopt sustainable practices.
FAQs
What is the difference between a linear and a circular economy?
A linear economy follows a ‘take, make, dispose’ model, where resources are used to make products that are eventually discarded. A circular economy, on the other hand, aims to keep resources in use for as long as possible through reuse, repair, remanufacturing, and recycling.
How can manufacturers contribute to a circular economy?
Manufacturers can contribute by adopting eco-design principles, implementing lean manufacturing processes, integrating renewable energy, and engaging in recycling and remanufacturing practices. These actions help reduce waste, improve resource efficiency, and lower environmental impacts.
Why is a circular economy important for sustainability?
A circular economy is crucial for sustainability because it reduces waste, conserves natural resources, and minimizes environmental pollution. By keeping materials in use for longer and designing out waste, we can create a more sustainable and resilient economy.
Conclusion
Creating a circular economy through sustainable practices in manufacturing is not just an environmental imperative but also a significant economic opportunity. By embracing principles like eco-design, lean manufacturing, renewable energy integration, and recycling, manufacturers can lead the way toward a more sustainable future. Companies like Patagonia, Interface, and Philips demonstrate that with innovation and commitment, a circular economy is achievable and beneficial for both businesses and the planet.
The transition may come with challenges, but the long-term benefits far outweigh the initial hurdles. As industries continue to innovate and adopt sustainable practices, the vision of a circular economy will become an increasingly tangible reality, driving us toward a more sustainable and prosperous future.


