In the dynamic landscape of global manufacturing, navigating tariffs and trade agreements has become a critical skill for businesses aiming to thrive in international markets. With geopolitical tensions and economic policies shaping the movement of goods across borders, understanding these factors is key to maintaining competitive advantage and ensuring sustainable growth. This article explores the intricate dance of tariffs and trade agreements, offering insights and strategies to help manufacturers navigate this complex terrain effectively.
Understanding Tariffs: The Basics
Tariffs, simply put, are taxes imposed on imported goods, typically by the government of the importing country. They serve various purposes, from protecting domestic industries to generating revenue for the government. For manufacturers, tariffs directly impact the cost of raw materials, components, and finished goods, influencing pricing strategies and profit margins.
Types of Tariffs
- Ad Valorem Tariffs: These tariffs are calculated as a percentage of the product’s value. For example, a 10% ad valorem tariff on electronics would mean paying an additional 10% of the product’s declared value upon importation.
- Specific Tariffs: Specific tariffs are fixed monetary amounts charged per unit of imported goods. They can vary depending on the product category and are less common than ad valorem tariffs.
- Compound Tariffs: Some countries apply a combination of ad valorem and specific tariffs to certain goods, creating a hybrid tariff structure that manufacturers must carefully assess.
Impact of Trade Agreements on Manufacturing
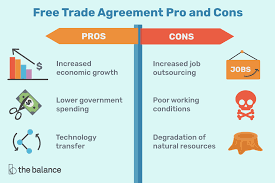
Trade agreements, on the other hand, are negotiated deals between countries to facilitate the movement of goods and services across borders with reduced or eliminated tariffs and other trade barriers. These agreements aim to promote economic cooperation and open markets, providing manufacturers with opportunities for cost savings and market expansion.
Benefits of Trade Agreements
- Tariff Reduction or Elimination: By participating in trade agreements like NAFTA or the EU Single Market, manufacturers can benefit from reduced tariffs or duty-free access to partner countries, making exports more competitive.
- Regulatory Harmonization: Trade agreements often include provisions for aligning regulatory standards, which simplifies compliance requirements for manufacturers exporting goods to multiple markets.
- Access to New Markets: Opening new markets through trade agreements enables manufacturers to diversify their customer base and reduce dependency on any single market, spreading risk effectively.
Image of Global Manufacturing: Navigating Tariffs and Trade Agreements

Challenges Faced by Manufacturers
While trade agreements offer significant advantages, they also present challenges that manufacturers must navigate carefully:
Compliance Complexity
- Rules of Origin: Manufacturers must comply with rules of origin requirements to qualify for preferential tariffs under trade agreements. Determining the origin of components and ensuring they meet specified criteria can be complex and requires meticulous record-keeping.
- Tariff Engineering: Some manufacturers engage in tariff engineering—modifying product designs or assembly processes—to meet rules of origin and maximize tariff benefits. This practice, while legal, demands strategic planning and operational flexibility.
Geopolitical Uncertainty
Navigating tariffs and trade agreements involves staying attuned to geopolitical developments that can swiftly impact international trade dynamics:
- Trade Wars: Escalating tariffs due to trade disputes, such as those seen between the US and China, can disrupt supply chains and increase manufacturing costs unexpectedly.
- Policy Changes: Changes in government administrations or shifts in national priorities may lead to revisions in trade policies, requiring manufacturers to adapt swiftly to new regulations and tariffs.
Strategies for Success in Global Manufacturing
To thrive in the face of tariff fluctuations and evolving trade agreements, manufacturers can adopt proactive strategies:
Diversification of Suppliers and Markets
- Supplier Networks: Building resilient supplier networks across different regions reduces dependency on any single source and mitigates the risk of supply chain disruptions due to tariffs or geopolitical tensions.
- Market Expansion: Actively exploring new markets through trade agreements diversifies revenue streams and positions manufacturers to capitalize on tariff reductions or preferential access benefits.
Continuous Monitoring and Adaptation
- Tariff Impact Analysis: Regularly assessing the impact of tariffs on production costs and pricing strategies enables manufacturers to adjust their operational and financial plans proactively.
- Policy Advocacy: Engaging in industry associations and advocacy groups can influence policymakers’ decisions on trade policies, advocating for regulations that support fair and open international trade practices.
FAQs: Clearing Common Doubts
Q: How do tariffs affect consumer prices? A: Tariffs can increase the cost of imported goods, which may lead manufacturers to raise prices to maintain profit margins, ultimately impacting consumer prices.
Q: Are all tariffs harmful to manufacturers? A: Not necessarily. Protective tariffs can shield domestic industries from foreign competition, supporting local manufacturing jobs and economic stability.
Q: How can small manufacturers compete with larger firms under trade agreements? A: Small manufacturers can leverage trade agreements to access new markets and benefit from reduced tariffs, leveling the playing field with larger competitors.
Conclusion: Navigating the Path Ahead
In conclusion, global manufacturing’s ability to navigate tariffs and trade agreements effectively hinges on strategic foresight, adaptability, and a deep understanding of international trade dynamics. By embracing the opportunities presented by trade agreements while mitigating the risks associated with tariffs, manufacturers can position themselves for sustained growth in a competitive global marketplace. As geopolitical landscapes evolve and economic policies shift, staying informed and agile will be essential for manufacturers aiming to thrive amidst uncertainty. With these insights and strategies in mind, manufacturers can chart a course towards resilience and prosperity in the realm of global manufacturing.
Through proactive planning, strategic partnerships, and advocacy for fair trade practices, manufacturers can navigate the complexities of tariffs and trade agreements, ensuring their businesses remain resilient and competitive in the global arena.


