Revolutionizing Small-Scale Manufacturing: CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution has come a long way since the days of large, sprawling factories that churned out massive quantities of goods. Today, the game is changing, and at the heart of this transformation are Power the CNC Machines Power the microfactory. What’s a CNC Machines Power the microfactory, you ask? It’s a scaled-down, hyper-efficient manufacturing setup that offers flexibility, precision, and customization, making it perfect for small businesses and startups.
Revolutionizing Small-Scale Manufacturing: CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution (Computer Numerical Control) machines are the workhorses behind this revolution, enabling small-scale manufacturers to produce high-quality products without needing massive resources. Ready to dive deeper? Let’s explore how CNC machines are fueling the CNC Machines Power the Microfactory movement and changing the landscape of small-scale manufacturing.
Table of Contents
What is a Microfactory?
A microfactory is exactly what it sounds like—an ultra-compact manufacturing facility designed to handle smaller production runs. Unlike traditional factories, which are geared toward mass production, microfactories focus on flexibility and customization. Think of it as a “factory in a box” that can fit into urban areas, home garages, or small industrial spaces. They’re perfect for businesses that need to manufacture unique, customized products in small quantities, without the overhead of a full-scale plant.
The Rise of Microfactory in Modern Manufacturing
In recent years, microfactory have emerged as a powerful alternative to traditional manufacturing models. Driven by the need for customization, efficiency, and sustainable practices, businesses across various industries are turning to microfactory to meet consumer demands. This rise is partly fueled by advancements in technology, including CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution , automation, and digital design tools.
Key Features of a Microfactory
Flexible Production Systems
One of the defining features of a microfactory is its flexibility. Since production is smaller and more focused, companies can quickly adjust to market demands. Whether it’s creating bespoke furniture, custom automotive parts, or even personalized electronics, microfactories can switch between production types without the headaches of traditional, large-scale operations.
Small Footprint, Big Impact
Microfactory are all about doing more with less. With a smaller physical footprint and a focus on efficiency, they can operate in spaces that were previously unimaginable for manufacturing facilities. You could have a microfactory running in a room smaller than your average office, yet producing precision components with the same quality as a large factory. And with fewer resources needed, they’re also more sustainable, reducing energy consumption and waste.
CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution: The Heart of the Microfactory
At the center of the microfactory revolution are CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution . These advanced tools allow manufacturers to produce precise, high-quality parts with minimal human intervention. But how exactly do CNC machines power microfactory? Let’s break it down.
How CNC Machines Work in a Microfactory
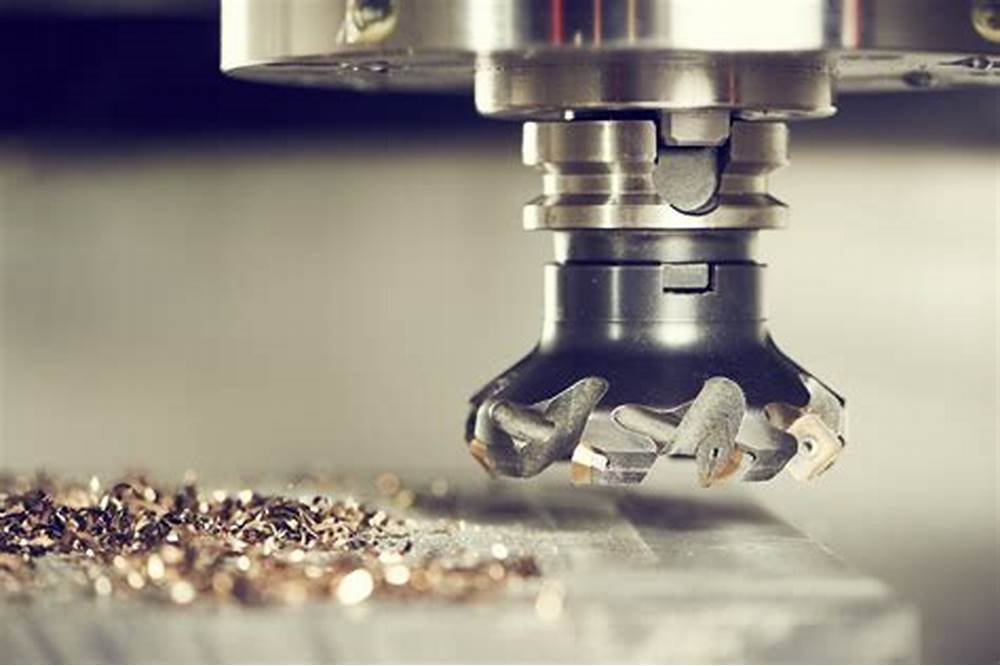

CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution operate using computer programming to control the movement of tools and machinery. In a microfactory setting, this automation is critical. Operators can input designs into the CNC machine, and it will cut, drill, or shape materials with extreme accuracy, following the exact specifications. The ability to replicate detailed work quickly makes CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution essential for microfactory looking to produce consistent, high-quality products on a small scale.
Types of CNC Machines Used in Small-Scale Manufacturing
CNC Milling Machines
CNC milling machines are common in microfactory for tasks that involve removing material from a workpiece. They’re used to cut metals, plastics, and even wood into precise shapes and parts, making them invaluable for industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
CNC Turning Machines
CNC turning machines are perfect for producing cylindrical parts, like screws, bolts, or any item that involves rotating materials. They’re used in a wide range of industries, including automotive, healthcare, and jewelry making.
CNC Routers
If you’re working with wood, plastic, or softer metals, a CNC router can be the ideal machine. It’s perfect for creating detailed designs, engraving, or cutting intricate shapes. These machines are particularly popular in the furniture and cabinetry industries, where precision and customization are key.
Benifites CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution


Precision and Efficiency
The precision of CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution is unmatched. They can work within tolerances as small as a fraction of a millimeter, ensuring that each part is identical. This level of accuracy not only improves the quality of the final product but also reduces errors and waste, making the process much more efficient.
Cost-Effective Production
CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution might have a high upfront cost, but in the long run, they save manufacturers a ton of money. Since the machines are automated, labor costs go down, and production times shorten. Plus, their ability to run continuously with minimal supervision means they can output more parts in less time compared to traditional methods.
Customization and Flexibility
Today’s customers demand more personalized products, and CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution enable that. Whether it’s creating custom jewelry, personalized home goods, or unique auto parts, CNC technology allows microfactory to pivot quickly and efficiently to meet specific customer needs. Flexibility is a huge selling point for small-scale manufacturers aiming to cater to niche markets.
How Microfactory are Revolutionizing Small-Scale Production
Empowering Small Businesses and Startups
Microfactory, powered by CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution, are leveling the playing field for small businesses and startups. Previously, manufacturing was often inaccessible due to the high costs of traditional factories. But with microfactory, entrepreneurs can now manufacture products with the same quality as large companies, all while maintaining control over production and customization. This access empowers more people to enter the manufacturing space, sparking innovation and creativity across industries.
Sustainable Manufacturing and Reducing Waste
In a world that’s increasingly conscious of sustainability, microfactories offer a greener alternative. With lean manufacturing techniques and CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution reducing material waste, these setups produce fewer byproducts and use less energy. This not only lowers the environmental footprint but also cuts down on costs, creating a win-win situation for both manufacturers and the planet.
Challenges in Adopting CNC-Powered Microfactory
High Initial Investment
While CNC machines offer long-term savings, the initial investment can be daunting for small businesses. These machines, along with the necessary software and training, require a significant upfront cost. However, with advancements in leasing options and government grants aimed at boosting local manufacturing, more businesses are finding ways to overcome this financial hurdle.
Skill Gaps and Training Requirements
Operating CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution isn’t a walk in the park—it requires skilled labor. For microfactory to thrive, workers need proper training in CNC programming, machine maintenance, and troubleshooting. This skill gap can sometimes slow down the adoption of CNC technology, but ongoing educational programs and online courses are helping bridge the gap.
The Future of CNC Machines and Microfactory
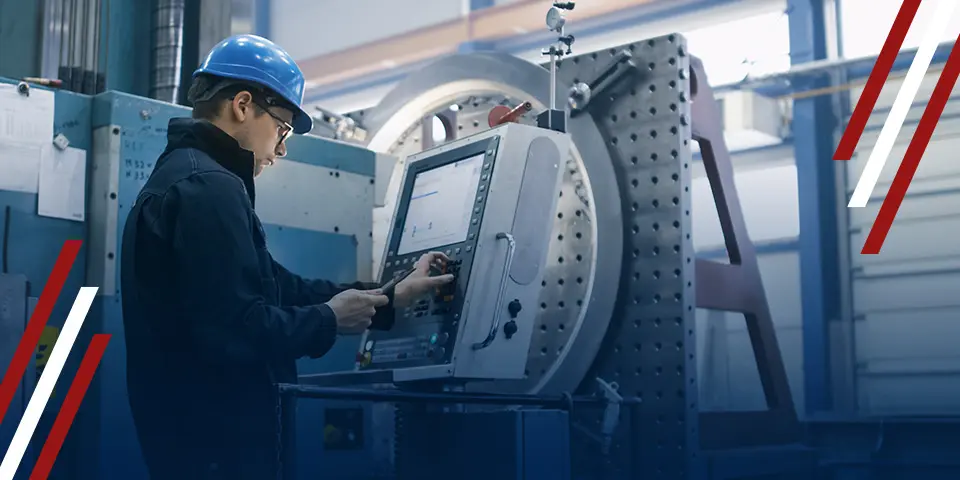
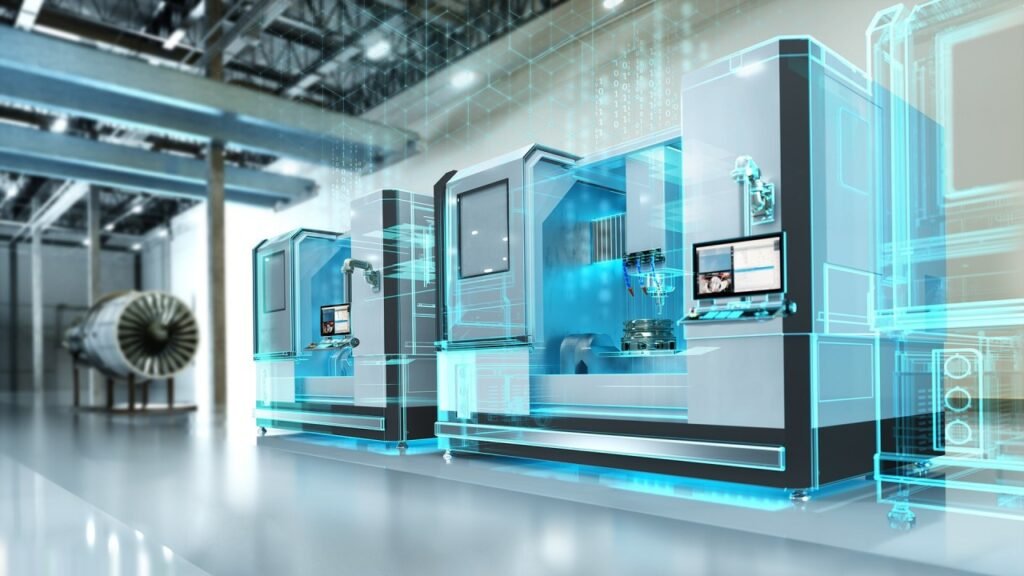


Advancements in Automation and AI
The future of CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution looks incredibly exciting, especially with the rise of automation and AI. Imagine machines that can diagnose their own problems, adjust production runs in real time, or even predict maintenance needs before they arise. These advancements will make microfactory even more efficient, reducing downtime and increasing output.
Global Impact on Supply Chains
As microfactory become more widespread, they could significantly impact global supply chains. By localizing production and reducing reliance on large factories in distant countries, businesses can cut down on shipping costs and delivery times. Plus, microfactory can produce on-demand, minimizing overproduction and waste.
How Microfactory Chooses the Right Material for CNC Machining
Choosing the right material for CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution is one of the most critical decisions in manufacturing, especially in a microfactory setup where precision, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness are key. Whether you’re producing automotive parts, electronic components, or custom furniture, selecting the appropriate material ensures that your end product meets the required specifications. But how do microfactory go about choosing the right material for CNC machining? Let’s explore the factors that influence material selection and why it’s so important for small-scale manufacturers.
Understanding CNC Machining and Material Compatibility


Before diving into material choices, it’s essential to understand CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution. CNC, or Computer Numerical Control, is a manufacturing process where pre-programmed computer software dictates the movement of machinery and tools. This precision allows for high-quality products, but the material being used plays a huge role in determining how successful the machining process will be.
Each material reacts differently to cutting, drilling, or shaping, and not every material is compatible with all CNC machines. That’s why selecting the right material is a foundational step in the production process.
Factors Influencing Material Selection in CNC Machining
1. Material Properties
The properties of a material directly impact how it behaves during machining. Microfactory consider factors such as:
- Hardness: Hard materials, like stainless steel or titanium, can be tough to machine but offer durability. On the other hand, softer materials, like plastics, are easier to shape but may not be as strong.
- Strength: The material’s tensile strength determines how much stress it can endure without breaking. This is crucial for parts that will be under heavy use, such as machine components or structural elements.
- Weight: Sometimes, a lighter material like aluminum is preferred for industries such as aerospace or electronics, where reducing weight can be just as important as maintaining strength.
- Thermal Conductivity: Some materials, such as metals, conduct heat well, which may influence their choice if heat dissipation is a factor.
- Corrosion Resistance: In industries where exposure to moisture or chemicals is common, choosing a material that resists corrosion, like certain stainless steels or plastics, is vital for product longevity.
2. Cost of Materials
In a microfactory, cost-efficiency is paramount. Choosing the right material often involves balancing performance with cost. High-end materials like titanium are excellent for strength and durability, but they come at a premium. Meanwhile, plastics or aluminum may provide enough performance at a fraction of the cost, making them more attractive for budget-conscious projects.
3. Machinability
Machinability refers to how easily a material can be cut, drilled, or shaped using CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution. Materials like brass, aluminum, and certain plastics have excellent machinability and are often favored in microfactory due to their ease of use. Harder materials, such as tool steel, require more advanced techniques and tools, potentially increasing both time and costs.
4. Surface Finish Requirements
Some products need a high-quality surface finish, such as those in the aerospace or medical device industries. If the finished part requires smooth surfaces or specific textures, the choice of material will impact how easily the required finish can be achieved. Metals like aluminum and stainless steel can be polished to a high sheen, while plastics may require different post-processing techniques.
5. Tolerance Levels
In CNC machining, tolerance refers to the degree of precision required for the dimensions of the part. Some materials are easier to machine to tight tolerances than others. Metals like aluminum and brass tend to hold tighter tolerances, while plastics can sometimes warp or change dimensions under different temperature conditions.
6. End-Use Application
The end use of the product is a major consideration when choosing a material. A microfactory might ask: Is the part for a medical device that needs biocompatibility? Is it for a car engine where it will be subjected to high heat? The specific use case will help narrow down the material options, as different materials excel in different environments and applications.
Common Materials Used in CNC Machining
CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution have a variety of materials at their disposal when working with CNC machines. Some of the most commonly used materials include:
Metals
1. Aluminum
Aluminum is one of the most widely used materials in CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution, especially in microfactory. It’s lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and highly machinable. Aluminum is ideal for industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics due to its balance of strength and weight.
2. Steel
Steel, particularly stainless steel, offers incredible strength and corrosion resistance. It’s often used in industries where durability is a priority, such as in medical equipment, automotive, and heavy machinery. While it’s harder to machine than aluminum, the benefits often outweigh the challenges in applications requiring toughness and longevity.
3. Brass
Brass is known for its excellent machinability and corrosion resistance, making it a top choice for applications requiring precision and intricate designs. It’s often used in plumbing, electrical components, and hardware due to its aesthetic appeal and ease of machining.
4. Titanium
Titanium is a high-strength, lightweight metal commonly used in industries like aerospace and medical due to its biocompatibility and corrosion resistance. However, its high cost and machinability challenges mean it’s often reserved for high-performance applications.
Plastics
1. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS is a durable and inexpensive plastic that’s commonly used in consumer goods, automotive parts, and toys. It’s easy to machine and can be post-processed with ease, making it a versatile choice for products where cost is a significant factor.
2. Polycarbonate
Polycarbonate is prized for its impact resistance and optical clarity, making it ideal for items like lenses, medical devices, and automotive components. While more challenging to machine than ABS, its durability makes it a popular choice.
3. Nylon
Nylon is a strong, flexible plastic commonly used in industrial applications. It’s resistant to wear and chemical damage, which makes it great for components like gears, bearings, and bushings. However, nylon can be tricky to machine due to its tendency to absorb moisture.
Material Testing and Prototyping in Microfactory
Once a microfactory narrows down its material options, prototyping and testing become essential. In this phase, small runs are produced using CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution to determine how well the material performs under real-world conditions. This testing phase can uncover potential issues, like material deformation or challenges with achieving the desired surface finish, which allows manufacturers to make adjustments before committing to full-scale production.
Balancing Sustainability and Performance
Today, sustainability is becoming a critical factor in material selection for many microfactory. Materials like recycled metals and biodegradable plastics are gaining popularity as businesses strive to reduce their environmental impact. While performance and cost remain top priorities, manufacturers are increasingly considering how the material lifecycle impacts the environment. This shift towards eco-friendly materials is shaping the future of CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution.
Conclusion
Microfactory, powered by CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution, are revolutionizing the world of small-scale manufacturing. These compact, flexible setups enable businesses to produce high-quality products with precision, efficiency, and sustainability. While there are challenges to adoption, including the initial investment and skill requirements, the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. As automation and AI continue to evolve, the future of microfactory looks bright, promising to empower small businesses, reduce environmental impact, and reshape global manufacturing processes.
FAQs
1. What industries benefit most from CNC-powered microfactory?
Microfactory are beneficial across industries like aerospace, automotive, healthcare, electronics, and even furniture manufacturing, where precision and customization are critical.
2. Are CNC machines difficult to operate?
CNC machines require training in programming and operation, but many educational programs and online courses are available to help users learn these skills.
3. How much does it cost to start a microfactory?
Costs vary, but initial investments for CNC Machines Power the Microfactory Revolution and software can be high. However, leasing options and government grants can help offset these costs.
4. Can microfactory help reduce environmental impact?
Yes! Microfactory are more sustainable due to their smaller footprint, lean manufacturing techniques, and reduced material waste.
5. Will automation replace human jobs in microfactory?
Automation will shift the focus from manual tasks to more skilled jobs, like CNC programming, machine maintenance, and troubleshooting, opening up new career opportunities.