The Importance of Risk Management in Manufacturing
Risk management in Manufacturing is like having a solid seatbelt in a car; it keeps you safe when the unexpected happens. In manufacturing supply chains, risk management is crucial because it helps companies prepare for and respond to potential disruptions, ensuring smooth operations and stability.
Table of Contents
Key Concepts in Risk Management
Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks followed by coordinated efforts to minimize their impact. It’s about being proactive rather than reactive. Think of it as setting up defenses in a game to prevent losing crucial points.
Understanding Manufacturing Supply Chains
Components of a Manufacturing Supply Chain
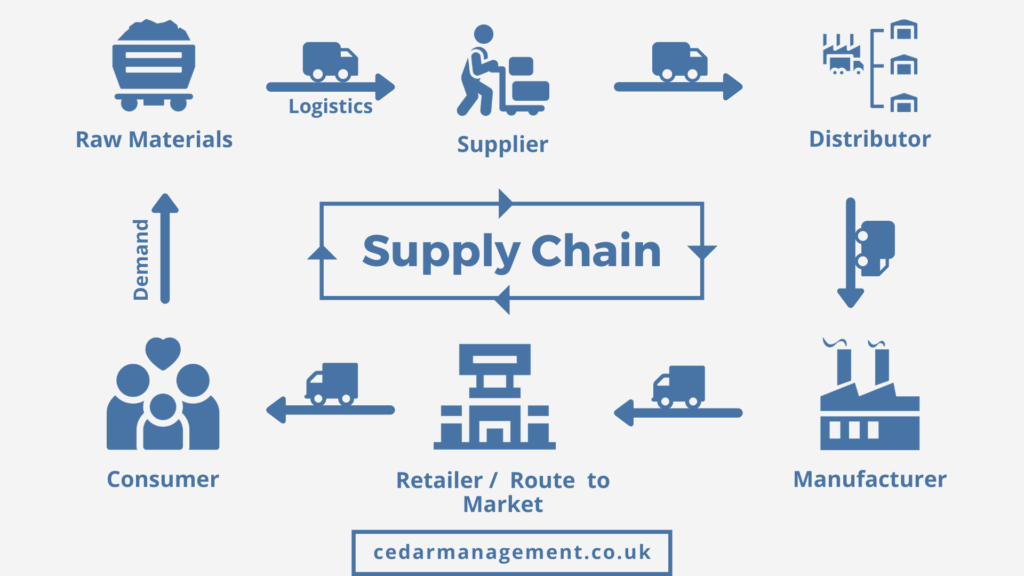
A manufacturing supply chain is a complex network of entities involved in producing and delivering a product. This includes suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. Each link in this chain plays a critical role, much like the gears in a clockwork mechanism.
Common Challenges in Supply Chains
Supply chains face various challenges such as supply shortages, logistical issues, and demand fluctuations. These issues can cause delays and increased costs, disrupting the entire process. It’s like trying to cook a meal with missing ingredients; it’s frustrating and can throw off your plans.
Types of Risks in Manufacturing Supply Chains
Operational Risks
Operational risks are related to the day-to-day functioning of the supply chain. These can include equipment failures, production delays, or workforce issues. Imagine your production line coming to a halt because of a broken machine; that’s an operational risk.
Financial Risks
Financial risks pertain to the monetary aspects of supply chains. These include fluctuations in currency exchange rates, credit risks, or unexpected costs. It’s like playing a game with unpredictable stakes; one misstep could lead to significant financial loss.
Strategic Risks
Strategic risks involve long-term planning and decisions. They include market competition, changes in consumer preferences, or geopolitical issues. It’s akin to navigating a ship through changing tides; you need to adjust your course based on future conditions.
Compliance Risks
Compliance risks are related to adhering to laws, regulations, and standards. Non-compliance can lead to legal issues, fines, and reputational damage. Think of it as following the rules in a game; ignoring them could result in penalties.
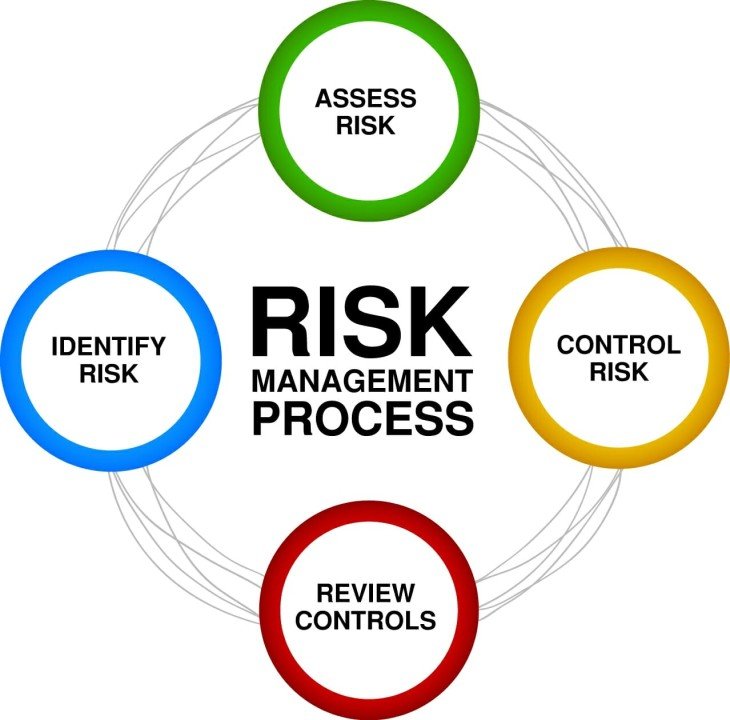
Risk Assessment and Analysis
Identifying Potential Risks
The first step in managing risk is identifying what could go wrong. This involves reviewing every aspect of the supply chain and pinpointing vulnerabilities. It’s like scanning a room for potential hazards before starting a project.
Evaluating Risk Impact and Likelihood
Once risks are identified, assessing their impact and likelihood helps prioritize them. For example, a risk with a high impact but low likelihood might be less urgent than a risk with a high likelihood but lower impact. This is akin to deciding which fire drills to prioritize based on the potential severity of each situation.

Qualitative vs. Quantitative Analysis
Risk analysis can be qualitative, focusing on subjective assessments, or quantitative, using numerical data. Qualitative analysis is more about expert opinions and scenarios, while quantitative relies on statistical models. It’s like choosing between a detailed narrative or a spreadsheet to understand potential risks.
Prioritizing Risks
After evaluating, the next step is to prioritize risks based on their potential impact and likelihood. This helps in focusing resources on the most critical areas. Think of it as triaging in a medical emergency; you deal with the most severe cases first.
Mitigation Strategies for Manufacturing Supply Chains
Developing Risk Mitigation Plans
Creating a risk mitigation plan involves outlining steps to reduce or manage identified risks. This plan should detail specific actions and contingency plans. It’s like drafting an emergency response plan; it prepares you for various scenarios.
Implementing Risk Control Measures
Once the plan is in place, implementing control measures is crucial. These can include improving processes, using advanced technology, or diversifying suppliers.
Process Improvements
Process improvements involve refining existing procedures to enhance efficiency and reduce risks. For instance, streamlining procurement processes can help avoid delays and cost overruns. It’s like upgrading your workflow to be more efficient and less prone to errors.
Technology Integration
Integrating technology, such as automation and real-time monitoring systems, can significantly mitigate risks. Technology helps in predicting potential issues and responding swiftly. Imagine having a smart assistant that alerts you to potential problems before they escalate.
The Role of Microfactory in Risk Management
What is a Microfactory?
A microfactory is a small-scale, modular manufacturing facility designed for flexibility and rapid production. These factories are typically more agile and can quickly adapt to changes or disruptions in the supply chain.
Benefits of Microfactory in Risk Management
Microfactories offer several benefits for risk management, including reduced dependency on large, centralized facilities and the ability to rapidly shift production in response to issues. They provide a more resilient and adaptable approach to manufacturing.
Case Studies and Examples
Several companies have successfully integrated microfactories into their supply chains. For example, some tech firms use microfactories to produce components closer to their end markets, reducing lead times and exposure to global supply chain risks.
Technology’s Impact on Risk Management
Role of Big Data and Analytics
Big data and analytics play a crucial role in risk management by providing insights into supply chain performance and potential vulnerabilities. Analyzing large datasets helps in predicting trends and making informed decisions.
Automation and Risk Reduction
Automation reduces human error and increases efficiency, which helps in mitigating operational risks. Automated systems can handle repetitive tasks and monitor processes in real-time, enhancing overall supply chain stability.
Best Practices for Effective Risk Management
Continuous Monitoring and Review
Regular monitoring and reviewing of risk management strategies are essential for adapting to new challenges. Continuous oversight helps in identifying emerging risks and updating mitigation plans accordingly.
Building a Risk-Aware Culture
Fostering a culture that prioritizes risk awareness among employees can significantly improve risk management. Training and encouraging staff to be vigilant and proactive helps in minimizing potential disruptions.
Conclusion
Effective risk management in manufacturing supply chains is essential for ensuring smooth operations and maintaining stability. By understanding and addressing various types of risks, implementing robust mitigation strategies, and leveraging modern technologies like microfactories, businesses can enhance their resilience against disruptions. Continuous monitoring and a proactive approach are key to navigating the complexities of today’s supply chains.
FAQs
1. What is a microfactory and how does it help in risk management?
A microfactory is a small, flexible manufacturing facility designed to adapt quickly to changes and disruptions. It helps in risk management by reducing dependency on large, centralized plants and enabling rapid production adjustments.
2. What are the main types of risks in manufacturing supply chains?
The main types of risks include operational risks, financial risks, strategic risks, and compliance risks. Each type affects different aspects of the supply chain and requires specific mitigation strategies.
3. How can technology improve risk management in manufacturing?
Technology improves risk management by providing real-time data and analytics, automating processes, and enhancing overall efficiency. This helps in predicting potential issues and responding more effectively.
4. Why is continuous monitoring important in risk management?
Continuous monitoring is crucial for adapting to new risks and updating mitigation strategies. It ensures that the risk management plan remains relevant and effective in the face of changing conditions.
5. What are some best practices for building a risk-aware culture in a company?
Best practices include providing regular risk management training, encouraging open communication about potential risks, and integrating risk awareness into daily operations. This helps employees stay vigilant and proactive.


