Role of Supply chain management (SCM) is the secret sauce behind every successful manufacturing operation. Whether you’re producing cars or gadgets, optimizing how materials, components, and finished goods flow is key to efficiency. But here’s the kicker: With the rise of the Role of Supply Chain microfactory model, the Role of Supply Chain is getting a revolutionary makeover. This article dives deep into how SCM is crucial for manufacturing efficiency and explores how microfactory are rewriting the rules.
Understanding Supply Chain Management (SCM)
What Is Role of Supply Chain Management?
At its core, supply chain management is all about overseeing and optimizing the flow of goods and services from raw material sourcing to finished product delivery. It involves everything from procurement, production planning, inventory management, and logistics. In manufacturing, the complexity of supply chains can vary, but their role remains critical—ensuring that the right materials get to the right place at the right time to meet customer demand.
Why SCM Is Crucial in Manufacturing
Manufacturers rely on well-oiled supply chains to maintain production efficiency, cut costs, and meet market demands. If your supply chain is sluggish or disjointed, it’s like a clog in a pipeline—everything slows down. Efficient SCM keeps production humming along smoothly, allowing businesses to stay competitive in a fast-paced market.
Key Components of a Successful Supply Chain
Procurement and Supplier Management
One of the first steps in SCM is sourcing the materials needed for production. This is where procurement and supplier management come into play. Having reliable suppliers and a strong procurement strategy ensures that manufacturers aren’t left waiting for parts or materials that could halt production.
Building Strong Supplier Relationships
Building strong, collaborative relationships with suppliers isn’t just about securing the lowest price. It’s about fostering trust and ensuring that suppliers understand your business’s evolving needs. Regular communication and collaboration are key to avoiding disruptions and achieving long-term efficiency.
Production Planning
Once you’ve got the materials, what’s next? Enter production planning and scheduling. This is the process of aligning production with customer demand while balancing capacity and inventory levels.
Balancing Demand and Role of Supply
The challenge? Forecasting demand accurately so that production lines aren’t sitting idle or churning out too much inventory. That’s where data analytics, demand planning, and supply chain visibility come into play—giving manufacturers the ability to forecast more precisely and plan accordingly.
Inventory Management
Managing inventory effectively is another essential component of SCM. Too much inventory leads to waste and increased costs, while too little can cause delays and missed opportunities.
Reducing Excess Inventory
The goal is to keep inventory levels lean, which not only cuts down on storage costs but also reduces the risk of excess stock becoming obsolete. By adopting practices like Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory, manufacturers can drastically reduce waste and improve efficiency.
SCM and Manufacturing Efficiency
Lean Manufacturing and SCM
Lean manufacturing principles are all about doing more with less—whether that’s time, resources, or energy. Supply chain management plays a huge role in achieving these lean goals by streamlining the flow of goods, reducing waste, and eliminating unnecessary steps in the process.
Streamlining Processes with Technology
Incorporating technology is a no-brainer when it comes to improving SCM. From advanced planning systems to real-time inventory tracking, tech is transforming the way supply chains operate.
Automation in Supply Chain Operations
Automation technologies such as robotics and AI-powered systems are increasingly used to handle repetitive supply chain tasks like inventory management and order processing. Not only does this speed up processes, but it also reduces human error and cuts down labor costs.
Role of Supply Chain Image
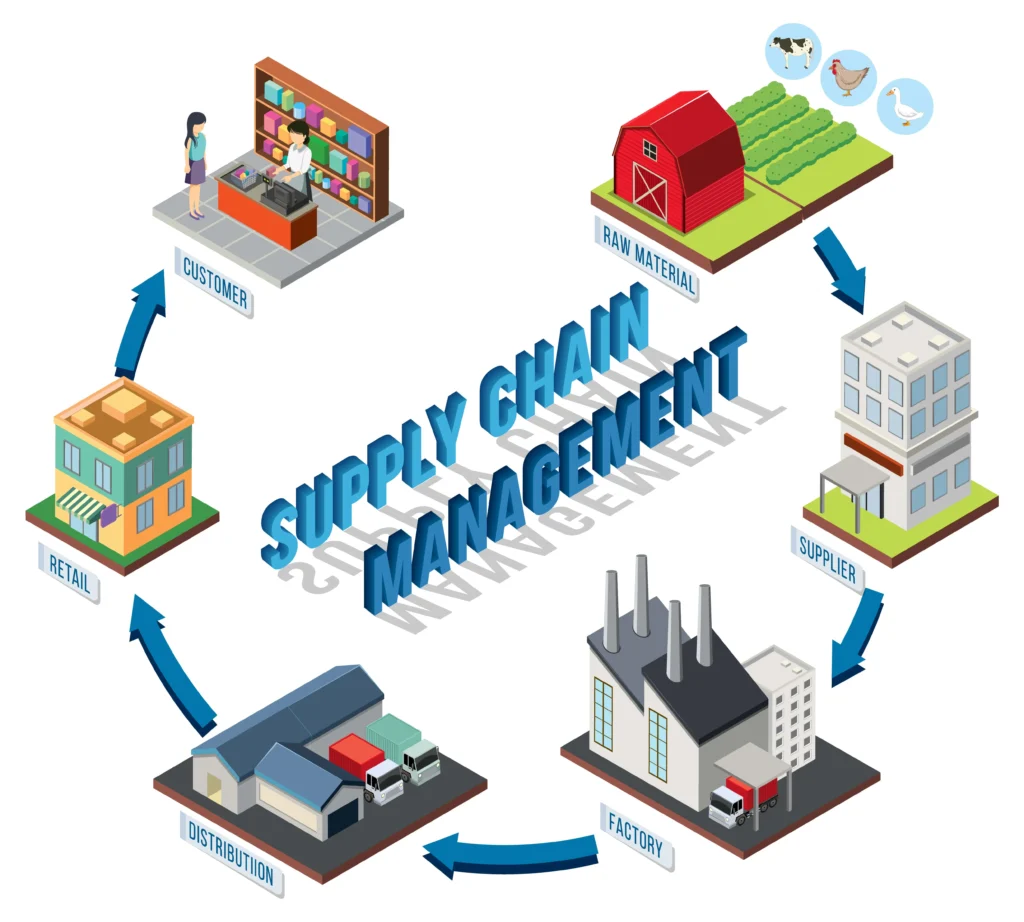


The Microfactory Revolution
What Is a Microfactory?
The concept of a microfactory might sound futuristic, but it’s already here. A microfactory is a highly automated manufacturing setup that requires significantly less space, energy, and resources than traditional factories. Microfactory often focus on producing custom or small-batch products, making them perfect for niche markets.
How Microfactory Are Transforming Manufacturing
Microfactories are shaking up the manufacturing world, particularly when it comes to SCM. Because they’re smaller and more agile, they can adapt quickly to changes in demand and supply. This means they require a much more flexible and responsive supply chain than traditional large-scale factories.
Benefits of Microfactory
Microfactories come with a ton of benefits: lower setup costs, reduced waste, energy efficiency, and shorter lead times. For manufacturers, this is a game-changer. By decentralizing production, microfactories make it easier to respond to local market needs, cut transportation costs, and reduce reliance on large, complex global supply chains.
SCM Strategies to Enhance Efficiency
Just-in-Time (JIT) Manufacturing
The JIT approach is a popular strategy for reducing inventory costs and increasing efficiency. By receiving goods only as they are needed in the production process, manufacturers can eliminate excess inventory and reduce waste.
Implementing Agile Supply Chain Techniques
Agility in supply chain management is all about flexibility—being able to adapt quickly to changes in demand, supply disruptions, or unexpected challenges. By adopting agile practices, manufacturers can stay nimble and better prepared to navigate the uncertainties of the modern marketplace.
The Impact of SCM on Reducing Costs
Lowering Operational Costs with SCM
Effective SCM isn’t just about speeding up production; it’s also a major cost-saving tool. By streamlining operations, reducing inventory, and optimizing logistics, manufacturers can drastically cut operational costs and increase profit margins.
Reducing Waste and Improving Sustainability
Sustainability is becoming a top priority in manufacturing, and SCM is central to these efforts. By improving resource utilization, cutting down on excess materials, and optimizing transportation routes, manufacturers can reduce their environmental footprint while also cutting costs.
Challenges in Supply Chain Management for Manufacturers
Global Supply Chain Disruptions
With the increasing complexity of global supply chains, disruptions are inevitable. Natural disasters, political instability, or unexpected events like the COVID-19 pandemic can throw a wrench into even the best-laid SCM plans. Managing these disruptions effectively is critical for maintaining efficiency.
Managing Uncertainty and Risk
Risk management in supply chains involves identifying potential threats and having contingency plans in place. Whether it’s a shortage of raw materials or a supplier issue, being proactive about risk can help manufacturers avoid costly delays and keep production moving smoothly.
The Future of Supply Chain Management in Manufacturing
Trends and Innovations Shaping the Future
Looking ahead, SCM will continue to evolve, with trends like digital supply chains, IoT, and blockchain leading the way. These innovations promise greater transparency, traceability, and collaboration across the entire supply chain.
The Role of AI and Data Analytics in SCM
AI and data analytics are becoming integral to SCM. By leveraging AI, manufacturers can forecast demand more accurately, optimize production schedules, and even predict potential disruptions before they happen. Data-driven insights provide a more strategic approach to supply chain management, helping manufacturers make smarter, faster decisions.
Conclusion
Supply chain management is the backbone of manufacturing efficiency. Whether you’re managing a traditional large-scale operation or exploring the possibilities of microfactories, an optimized supply chain is key to staying competitive. From streamlining processes with technology to embracing the agile and lean manufacturing principles, SCM plays a critical role in minimizing waste, reducing costs, and maximizing output. As manufacturing continues to evolve, SCM will remain at the forefront of this transformation, driving the industry towards greater efficiency and sustainability.
FAQs
1. What is supply chain management in manufacturing? Supply chain management in manufacturing involves overseeing and optimizing the flow of materials, goods, and information from suppliers to end consumers to improve production efficiency.
2. How do microfactory impact traditional supply chains? Microfactories require a more agile and flexible supply chain, as they focus on smaller, more localized production. This leads to shorter lead times and reduced transportation costs.
3. What is the role of technology in supply chain management? Technology plays a crucial role in SCM by automating processes, improving inventory management, and providing real-time data for better decision-making.
4. How can manufacturers reduce waste through SCM? Manufacturers can reduce waste by implementing strategies like lean manufacturing, Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory, and by improving resource utilization throughout the supply chain.
5. What are some challenges in supply chain management? Common challenges include global supply chain disruptions, managing uncertainty, and dealing with issues like raw material shortages or political instability.


