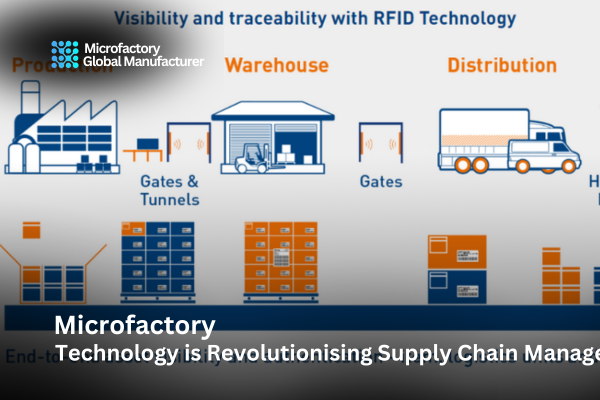
Technology is Revolutionising Supply chain management (SCM) is like the backstage crew of a grand performance; it’s the unsung hero that ensures everything runs smoothly. It involves the coordination of all activities required to produce and deliver a product, from raw materials to final delivery. In manufacturing, SCM is crucial because it directly impacts efficiency, cost, and customer satisfaction.
What is Technology is Revolutionising Supply Chain Management?
At its core, Technology is Revolutionising Technology is Revolutionising Supply Chain Management is the management of the flow of goods and services. It encompasses everything from procurement of raw materials, production, logistics, and distribution. Effective SCM ensures that products are made and delivered to customers in the most efficient way possible.
Why It Matters in Manufacturing
In manufacturing,Technology is Revolutionising Supply Chain Management can make or break a business. Efficient Supply Chain Management reduces costs, improves quality, and speeds up production times. It helps manufacturers meet demand without overstocking or understocking, balancing supply and demand perfectly.
The Role of Technology in Modern Technology is Revolutionising Supply Chains
Technology has become the backbone of modern supply chains. From automation to AI, tech innovations are transforming how supply chains operate, making them faster, more efficient, and more adaptable.
Future Of Technology is Revolutionising Supply Chain Management
The future of supply chain management (SCM) is poised for significant transformation as technology continues to evolve rapidly. Here are some key trends and developments that are likely to shape the future of supply chains:
1. Increased Use of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and ML will play a larger role in optimizing supply chain operations by providing predictive analytics, improving demand forecasting, and automating decision-making. These technologies will allow companies to anticipate disruptions, adjust production schedules, and minimize risks in real-time.
2. Blockchain for Transparency and Traceability
Blockchain technology will enhance transparency and trust in supply chains by providing a decentralized and immutable ledger of transactions. This will enable better tracking of products, ensuring authenticity, and reducing fraud. Blockchain will be particularly impactful in industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and luxury goods.
3. Autonomous Vehicles and Drones
Autonomous trucks and drones are expected to revolutionize the logistics sector by reducing delivery times, cutting labor costs, and improving efficiency. These technologies will enable faster last-mile delivery, especially in urban areas, and reduce dependency on human drivers.
4. Advanced Robotics in Warehousing and Manufacturing
Robotics will continue to automate tasks in warehouses and manufacturing plants, increasing efficiency and accuracy. Collaborative robots, or “cobots,” will work alongside humans, enhancing productivity without fully replacing human workers.
5. Internet of Things (IoT) for Real-Time Monitoring
The IoT will enable more connected and intelligent supply chains by providing real-time monitoring of goods, equipment, and vehicles. This will lead to better visibility, faster response times, and predictive maintenance, ensuring fewer disruptions.
6. 3D Printing for On-Demand Manufacturing
3D printing (also known as additive manufacturing) will become a key part of supply chains, allowing companies to produce products on demand. This will reduce the need for large inventories, minimize shipping costs, and speed up time to market.
7. Microfactory and Localized Production
The rise of microfactory and localized production will shorten supply chains by enabling companies to manufacture products closer to the end consumer. This reduces transportation costs, minimizes environmental impact, and allows for more customization and faster response to market changes.
8. Sustainable and Green Supply Chains
As sustainability becomes a top priority, future supply chains will focus on reducing environmental impact. This will include adopting eco-friendly packaging, optimizing routes for lower carbon emissions, and partnering with sustainable suppliers. Circular supply chains that emphasize recycling and reuse will also gain importance.
Automation and Robotics
Automation and robotics are like the superheroes of modern manufacturing. They streamline repetitive tasks, reduce human error, and increase production speed.
Technology is Revolutionising Supply Chain Management Image



Benefits of Automation
Automation brings several benefits:
- Increased Efficiency: Machines can work faster and more accurately than humans.
- Cost Savings: Reduces labor costs and minimizes errors that can lead to costly rework.
- Consistency: Ensures uniform quality and precision in manufacturing processes.
Challenges and Considerations
However, automation isn’t without its challenges:
- High Initial Costs: Investing in advanced machinery can be expensive.
- Training Needs: Employees need to be trained to work alongside automated systems.
- Maintenance: Automated systems require regular maintenance and troubleshooting.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are like the brainpower behind modern supply chains. They analyze vast amounts of data to make predictions and optimize processes.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses historical data to forecast future trends. For instance, it can predict demand surges or supply shortages, allowing manufacturers to adjust their strategies proactively.
AI-Driven Decision Making
AI helps in making more informed decisions by analyzing data patterns and providing insights that humans might miss. This leads to better inventory management, improved supply chain visibility, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) connects devices and systems, allowing them to share data in real-time. This connectivity enhances supply chain visibility and control.
Real-Time Data and Tracking
IoT provides real-time tracking of goods and materials. This means manufacturers can monitor shipments, track inventory levels, and identify potential disruptions instantly.
Improving Efficiency with IoT
IoT helps in optimizing various aspects of the supply chain, such as improving warehouse management, streamlining production processes, and reducing downtime through predictive maintenance.
Microfactory: A Game-Changer in Manufacturing
Microfactory are transforming manufacturing by focusing on small-scale, highly flexible production units. They are like the agile ninjas of the manufacturing world, capable of adapting quickly to changes in demand and production needs.
What is a Microfactory?
A microfactory is a small-scale, modular manufacturing facility designed to produce limited quantities of products with high precision and flexibility. It leverages advanced technologies like robotics, IoT, and AI to operate efficiently.
Advantages of Microfactory
Microfactory offer several advantages:
- Flexibility and Agility: They can quickly adapt to changes in production needs or market demands.
- Local Production Benefits: Reduces transportation costs and environmental impact by producing goods closer to the consumer.
Integrating Technology with Microfactory
Combining technology with microfactory enhances their capabilities and effectiveness.
Smart Microfactory
Smart microfactory use connected systems and data sharing to optimize operations. They integrate IoT, AI, and robotics to create a highly efficient and responsive manufacturing environment.
Connected Systems and Data Sharing
By connecting different systems and sharing data across the microfactory, manufacturers can improve coordination, enhance quality control, and streamline production processes.
Enhanced Quality Control
Advanced technologies enable better quality control by monitoring production processes in real-time, detecting defects early, and ensuring consistent product quality.
Future Trends in Supply Chain Technology
As technology continues to evolve, the future of supply chain management looks promising.
Emerging Technologies
New technologies such as blockchain, augmented reality (AR), and advanced analytics are expected to further revolutionize supply chain management. These innovations will enhance transparency, improve traceability, and streamline operations.
The Impact of 5G on Supply Chains
5G technology will play a significant role in supply chain management by enabling faster data transfer, improving connectivity, and supporting real-time communication and decision-making.
Conclusion
Technology is dramatically changing the landscape of supply chain management in manufacturing. From automation and AI to IoT and microfactory, these advancements are making supply chains more efficient, flexible, and responsive. As we move forward, staying updated with emerging technologies will be key to maintaining a competitive edge and meeting the ever-evolving demands of the market.
FAQs
1. What is the role of AI in supply chain management? AI helps analyze large volumes of data to make informed decisions, predict trends, and optimize supply chain processes.
2. How do microfactory affect local economies? Microfactory boost local economies by creating jobs, reducing transportation costs, and supporting local businesses.
3. What are the key benefits of using IoT in manufacturing? IoT provides real-time data, improves tracking and efficiency, enhances predictive maintenance, and optimizes inventory management.
4. How can automation improve manufacturing processes? Automation increases production speed, reduces errors, lowers labor costs, and ensures consistent quality.
5. What future trends should we expect in supply chain technology? Future trends include the adoption of blockchain, augmented reality, advanced analytics, and the widespread impact of 5G technology.