Ever wondered how those perfectly uniform pasta shapes, sleek aluminum window frames, or intricate plastic pipes are made? The answer lies in a manufacturing process called extrusion. It’s one of those behind-the-scenes marvels that we rarely think about but is crucial to countless products we use daily. Let’s dive into the world of extrusion and see what it’s all about.
What is Extrusion?
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile. A material is pushed through a die of the desired cross-section. Think of it like squeezing toothpaste out of a tube – that’s extrusion in its simplest form! This technique is used widely across industries to produce a variety of products from metals, plastics, ceramics, and even food.
Types of Extrusion
There are two main types of extrusion:
- Hot Extrusion: This involves heating the material to make it more pliable. It’s often used for metals like aluminum, copper, and steel. Heating makes it easier to push through the die, reducing wear and tear on the machinery and making the process more efficient.
- Cold Extrusion: As the name suggests, this is done at or near room temperature. It’s commonly used for materials like lead, tin, and aluminum alloys. Cold extrusion can strengthen the material through work hardening and produce a better surface finish.
How Does Extrusion Work?
The Basic Steps of Extrusion
Let’s break down the steps of a typical extrusion process:
- Preparation: The raw material, known as the billet, is prepared. This could involve heating it if it’s a hot extrusion process.
- Feeding the Billet: The billet is placed into the extrusion press. In hot extrusion, it’s heated to the desired temperature.
- Extrusion Press: A powerful ram pushes the billet through a die, shaping it into the desired cross-sectional profile. The die is a tool that determines the shape and size of the extruded product.
- Cooling: Once the material exits the die, it’s cooled down. This is crucial, especially for metals, to ensure they retain the correct shape and properties.
- Cutting and Finishing: The extruded material is cut to the required length and might undergo further finishing processes like anodizing, painting, or machining.
Tools of the Trade
- Die: The heart of the extrusion process. It’s a specially designed tool that shapes the material as it’s pushed through.
- Ram: The component that applies the force to push the billet through the die.
- Extrusion Press: The machine that houses the ram and die and provides the necessary force.
Applications of Extrusion
Extrusion is incredibly versatile and used in many industries. Here are some common applications:
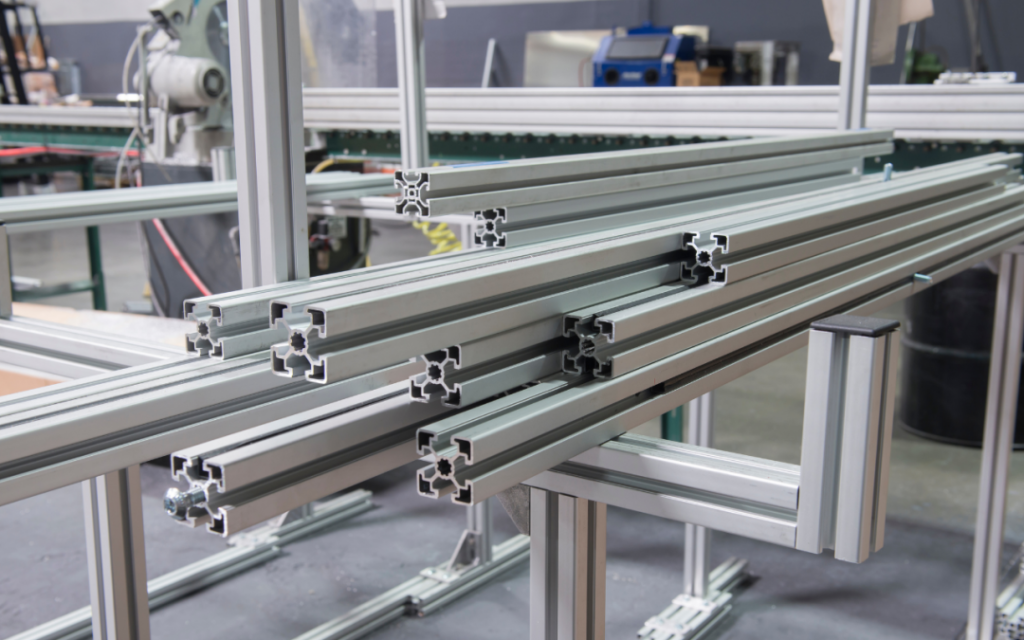
Metal Extrusions
- Construction: Aluminum window frames, structural components.
- Automotive: Engine parts, chassis components.
- Electronics: Heat sinks, housings.
Plastic Extrusions
- Packaging: Bottles, containers.
- Piping: Plumbing pipes, conduit.
- Consumer Goods: Toys, household items.
Food Extrusions
- Snacks: Cereal, pasta shapes.
- Pet Food: Kibble, treats.
Ceramics and Beyond
- Industrial: Insulators, technical ceramics.
- Medical: Prosthetics, implants.
images for extrusions


Benefits of Extrusion
So, why is extrusion such a popular manufacturing method? Here are some key benefits:
- Efficiency: The continuous process allows for high-volume production.
- Flexibility: Can create complex cross-sections and intricate shapes.
- Material Utilization: Less material wastage compared to other methods.
- Strength and Consistency: Especially with metals, extrusion can enhance material properties.
Challenges and Limitations
Of course, extrusion isn’t without its challenges. Some common issues include:
- Die Wear: Constant pressure and heat can wear out dies, requiring regular replacement.
- Material Limitations: Not all materials are suitable for extrusion, especially those with low ductility.
- Size Constraints: There are limits to the size and thickness of extruded products.
FAQs About Extrusion
What materials can be extruded?
Most commonly, metals (like aluminum and copper), plastics, and ceramics. Even food can be extruded!
Is extrusion a sustainable process?
Yes, it can be quite sustainable. For example, aluminum extrusion uses less energy compared to other metal forming processes and allows for recycling of scrap material.
Can complex shapes be made using extrusion?
Absolutely! One of the biggest advantages of extrusion is its ability to create complex cross-sectional shapes.
How does extrusion compare to injection molding?
Extrusion is typically used for continuous profiles like pipes and rods, whereas injection molding is used for complex, discrete parts like toys and car parts.
Conclusion
Extrusion is a fascinating and incredibly versatile manufacturing process that plays a crucial role in our daily lives. From the aluminum frames that support our windows to the cereal we pour into our breakfast bowls, extrusion is behind it all. It’s a process that combines efficiency, flexibility, and precision, making it indispensable in various industries.
So, next time you admire a sleek piece of metalwork or munch on a perfectly shaped snack, you’ll know the magic of extrusion at work. Isn’t it amazing how much goes on behind the scenes to create the things we often take for granted? Now that you know what extrusion is and how it works, you can appreciate the ingenuity and engineering that shapes our world.