In the dynamic world of manufacturing, precision is key. Whether you’re designing the latest gadget or developing intricate components, the ejection process plays a critical role in ensuring your products are flawless. Ejection modelling, often overlooked, is an essential aspect of manufacturing that guarantees the seamless removal of parts from molds without damage or deformation. This guide delves into the complete process of ejection modelling, offering a thorough understanding to both beginners and seasoned professionals.
Understanding Ejection Modelling
What is Ejection Modelling?
Ejection modelling involves designing and simulating the mechanisms that eject a part from a mold after the manufacturing process. This step is crucial as improper ejection can lead to defects, increased scrap rates, and inefficiencies in production.
Why is it Important?
- Quality Assurance: Proper ejection ensures the part maintains its integrity and dimensions.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces scrap and rework costs.
- Production Speed: Enhances the efficiency of the manufacturing process, reducing cycle times.
The Complete Process of Ejection Modelling
1. Initial Design Considerations
The first step in ejection modelling is to consider the design of the part and the mold. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- Draft Angles: Incorporating appropriate draft angles in your design can facilitate easier ejection.
- Surface Finish: A smooth surface finish reduces friction during ejection.
- Material Selection: The material of both the part and the mold can affect the ejection process.
2. Choosing the Right Ejection System
There are various ejection systems available, and choosing the right one depends on the specifics of your project. Common ejection systems include:
- Pin Ejectors: Simple and cost-effective, suitable for most applications.
- Sleeve Ejectors: Ideal for hollow or cylindrical parts.
- Blade Ejectors: Used for thin-walled or delicate parts.
- Air Ejectors: Utilizes compressed air, perfect for fragile components.
3. Simulation and Analysis
Before moving to production, it’s crucial to simulate the ejection process using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) and CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) software. This helps in:
- Identifying Potential Issues: Detects any areas where the part might stick or deform.
- Optimizing Ejection Force: Ensures the force applied is sufficient but not excessive.
- Testing Different Scenarios: Allows for adjustments and refinements without physical trials.
4. Prototype Testing
Creating a prototype and testing the ejection system in real-world conditions provides valuable insights. It helps in validating the design and making any necessary modifications.
5. Final Adjustments and Production
Based on the results from prototype testing, make any final adjustments to the ejection system. Once everything is fine-tuned, the process can move into full-scale production.
Image of Complete Process of ejection modelling
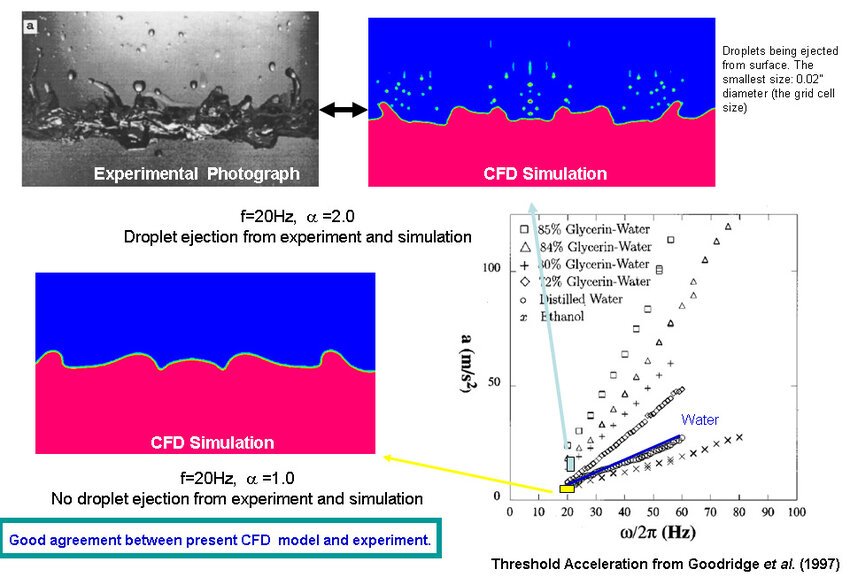
Practical Tips for Effective Ejection Modelling
- Regular Maintenance: Keep the ejection system and mold clean and well-maintained to avoid unexpected issues.
- Monitoring and Feedback: Continuously monitor the ejection process and gather feedback to make improvements.
- Stay Updated: Technology and methods in ejection modelling are constantly evolving. Stay informed about the latest advancements and incorporate them into your process.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Warping and Deformation
Challenge: Parts can warp or deform during ejection due to uneven forces. Solution: Ensure uniform application of ejection force and use simulation software to predict and mitigate these issues.
Sticking in the Mold
Challenge: Parts sticking in the mold can lead to damage and inefficiencies. Solution: Use appropriate draft angles and surface finishes, and consider using mold release agents if necessary.
Insufficient Ejection Force
Challenge: If the ejection force is too low, parts might not eject properly. Solution: Adjust the ejection force through simulation and testing to find the optimal balance.
FAQs
What is the role of draft angles in ejection modelling?
Draft angles facilitate the easy removal of parts from molds by reducing friction and resistance during ejection. They are essential for preventing damage and ensuring smooth ejection.
How can simulation software aid in the ejection modelling process?
Simulation software allows for virtual testing of the ejection process, helping to identify potential issues and optimize the design before physical production. It saves time and resources by reducing the need for multiple physical prototypes.
What are some common materials used for molds in ejection modelling?
Common materials include hardened steel, aluminum, and certain types of plastics, depending on the application and production volume. The choice of material affects the durability and performance of the mold.
Can ejection systems be automated?
Yes, many modern ejection systems are automated, allowing for precise control and consistency in the ejection process. Automation can enhance efficiency and reduce human error.
Conclusion
Mastering the complete process of ejection modelling is essential for anyone involved in manufacturing and engineering. By understanding the intricacies of design, choosing the right ejection system, leveraging simulation tools, and conducting thorough testing, you can ensure high-quality production with minimal defects. Stay informed, embrace new technologies, and continuously refine your processes to excel in the ever-evolving field of ejection modelling. Whether you’re a novice or a seasoned professional, these insights will guide you toward more efficient and effective manufacturing practices.


